

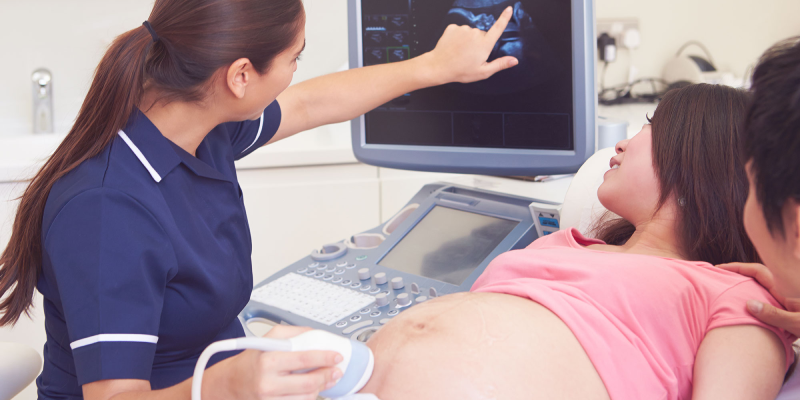
Ultrasound (also called sonogram) is a prenatal test offered to most pregnant women. It uses sound waves to show a picture of your baby in the uterus (womb). Ultrasound helps your health care provider check on your baby’s health and development.
Ultrasound can be a special part of pregnancy—it’s the first time you get to “see” your baby! Depending on when it’s done and your baby’s position, you may be able to see his hands, legs and other body parts. You may be able to tell if your baby’s a boy or a girl, so be sure to tell your provider if you don’t want to know!
Most women get an ultrasound in their second trimester at 18 to 20 weeks of pregnancy. Some also get a first-trimester ultrasound (also called an early ultrasound) before 14 weeks of pregnancy. The number of ultrasounds and timing may be different for women with certain health conditions like as asthma and obesity.
Talk to your provider about when an ultrasound is right for you.
Your provider uses ultrasound to do several things, including:
Your provider also uses ultrasound for screening and other testing. Screening means seeing if your baby is more likely than others to have a health condition; it doesn’t mean finding out for sure if your baby has the condition.
Your provider may use ultrasound:
Transabdominal ultrasound :When you hear about ultrasound during pregnancy, it’s most likely this kind. You lay on your back on an exam table, and your provider covers your belly with a thin layer of gel. The gel helps the sound waves move more easily so you get a better picture. Then he moves the transducer across your belly. You may need to drink several glasses of water about 2 hours before the exam to have a full bladder during the test. A full bladder helps sound waves move more easily to get a better picture. Ultrasound is painless, but having a full bladder may be uncomfortable. The ultrasound takes about 20 minutes.
Transvaginal ultrasound :This kind of ultrasound is done through the vagina (birth canal). You lay on your back on an exam table with your feet in stirrups. Your provider moves a thin transducer shaped like a wand into your vagina. You may feel some pressure from the transducer, but it shouldn’t cause pain. Your bladder needs to be empty or just partly full. This kind of ultrasound also takes about 20 minutes.
In special cases, your provider may use these kinds of ultrasound to get more information about your baby:
Doppler ultrasound :This kind of ultrasound is used to check your baby’s blood flow if he’s not growing normally. Your provider uses a transducer to listen to your baby’s heartbeat and to measure the blood flow in the umbilical cord and in some of your baby’s blood vessels. You also may get a Doppler ultrasound if you have Rh disease. This is a blood condition that can cause serious problems for your baby if it’s not treated. Doppler ultrasound usually is used in the last trimester, but it may be done earlier.
3-D ultrasound :A 3-D ultrasound takes thousands of pictures at once. It makes a 3-D image that’s almost as clear as a photograph. Some providers use this kind of ultrasound to make sure your baby’s organs are growing and developing normally. It can also check for abnormalities in a baby’s face. You also may get a 3-D ultrasound to check for problems in the uterus.
4-D ultrasound :This is like a 3-D ultrasound, but it also shows your baby’s movements in a video.
Ultrasound is safe for you and your baby when done by your health care provider. Because ultrasound uses sound waves instead of radiation, it’s safer than X-rays. Providers have used ultrasound for more than 30 years, and they have not found any dangerous risks.
If your pregnancy is healthy, ultrasound is good at ruling out problems, but it can’t find every problem. It may miss some birth defects. Sometimes, a routine ultrasound may suggest that there is a birth defect when there really isn’t one. While follow-up tests often show that the baby is healthy, false alarms can cause worry for parents.
You may know of some places, like stores in a mall, that aren’t run by doctors or other medical professionals that offer “keepsake” 3-D or 4-D ultrasound pictures or videos for parents. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG), the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the American Institute of Ultrasound in Medicine (AIUM) do not recommend these non-medical ultrasounds. The people doing them may not have medical training and may give you wrong or even harmful information.
For most women, ultrasound shows that the baby is growing normally. If your ultrasound is normal, just be sure to keep going to your prenatal check-ups.
Sometimes, ultrasound may show that you and your baby need special care. For example, if the ultrasound shows your baby has spina bifida, he may be treated in the womb before birth. If the ultrasound shows that your baby is breech (feet-down instead of head-down), your provider may try to flip your baby’s position to head-down, or you may need to have a caesarean section (also called c-section). A c-section is surgery in which your baby is born through a cut that your doctor makes in your belly and uterus.
No matter what an ultrasound shows, talk to your provider about the best care for you and your baby.