
An abdominal laparoscopy is also known as a diagnostic laparoscopy. It is a surgical procedure used to examine the organs inside the abdomen and other closed spaces, like the knees. Abdominal Laparoscopy is a completely safe and minimally invasive procedure that involves small incisions. During an abdominal laparoscopy, a doctor uses a special tool called a laparoscope to view the abdominal organs. The laparoscope is a tool which is long, thin tube with a bright light and a high-resolution camera at the front. It is inserted through a small incision in the abdominal wall. As it moves along, the camera captures images that are displayed on a video monitor.
A laparoscopy allows the expert to see inside your body in real time, without having to make large incisions. He can also obtain biopsy samples during this procedure, as well as also perform surgery.
An abdominal laparoscopy is commonly performed to identify and diagnose the cause of pelvic or abdominal pain. It is usually done when other noninvasive methods are not effective in providing a diagnosis.
Abdominal problems can also be diagnosed using the following imaging techniques:
A laparoscopy is performed when these tests do not provide sufficient information or clarity for a diagnosis. The procedure may also be used to take a biopsy, which is a sample of tissue, from a specific organ in the abdomen.
The most common risks associated with it are: bleeding, infection, and damage to organs in the abdomen. However, these rarely happen.After your procedure, it’s important to watch for any symptoms of infection. Contact us if you experience any of the following symptoms:
In some cases, your surgeon may decide that the risk of a diagnostic laparoscopy is too high compared to the benefits of using a minimally invasive approach. This often happens if you have a history of abdominal surgeries, which increases the risk of adhesions forming between abdominal structures. Performing laparoscopy in the presence of adhesions can take longer and raises the risk of organ injury.
You should tell the expert consultant about any prescription or over-the-counter medications you’re taking. He will tell you how they should be used before and after the procedure. He may also change the dose of any medications that could affect the outcome of a laparoscopy.
You should also tell clearly if you’re pregnant or think you might be pregnant. It is so because this will reduce the risk of harm to your developing baby.
You’ll probably need to avoid eating and drinking for at least 8 hours before a laparoscopy. You should also arrange for someone who can drive you home after the procedure is completed. Because the use of general anesthesia can make you feel drowsy and unable to drive for several hours after surgery.
An abdominal laparoscopy is usually an outpatient procedure. It means that you can go home the same day. It may be done in a hospital or an outpatient surgical center.
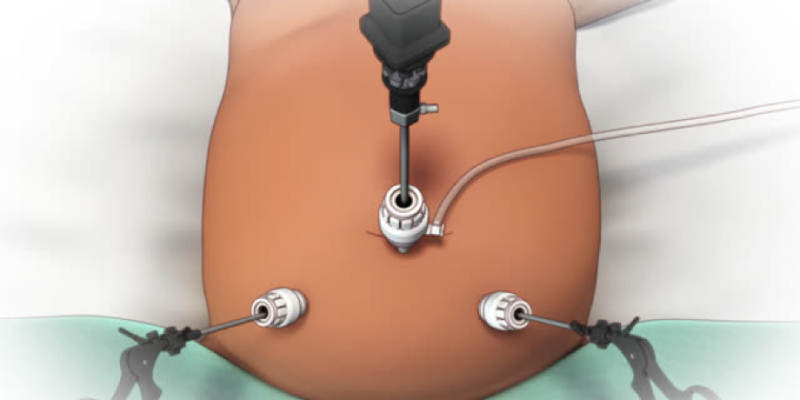
You will usually receive general anesthesia for this surgery, which means you will be asleep and won't feel any pain. In order to deliver medication and fluids, an IV line will be inserted. During the laparoscopy, the surgeon makes a small incision. This will be below your belly button and then inserts a tube called a cannula. The cannula is used to fill your abdomen with carbon dioxide gas, which helps provide a clearer view of your organs.
Once the abdomen is inflated, the surgeon inserts a laparoscope through the incision. The laparoscope has a camera that displays real-time images of your organs on a screen.
The number and size of incisions depend on the specific purpose of the surgery. Usually, there are one to four small incisions, each about 1 to 2 centimeters long. These incisions further helps other instruments to be inserted if needed, such as for a biopsy to collect a small tissue sample for evaluation.
After completing the procedure the instruments are removed. The incisions are closed with the help of stitches or surgical tape. Bandages may be applied over the incisions.
After the surgery, you will be monitored for several hours before being discharged from the hospital. You will be observed closely, and any adverse reactions or bleeding will be checked. The length of your hospital stay will depend on your overall health and how your body responds to the surgery. Sometimes an overnight stay is required.
If you received general anesthesia, you will need someone to drive you home. It takes a few hours for the effects of anesthesia to wear off, so driving yourself is not safe. In the days following the laparoscopy, you may experience moderate pain and throbbing around the incision sites. The pain should improve within a few days, and you may be prescribed pain medication. It is common to have shoulder pain after the procedure due to the carbon dioxide gas used to inflate the abdomen. The gas can irritate the diaphragm, which shares nerves with the shoulder. This discomfort should subside within a couple of days. Bloating may also occur.
Within a week, you can usually resume all normal activities. A follow-up appointment will be scheduled around 2 weeks after the laparoscopy.
To aid in a smoother recovery, consider the following:
When a biopsy is performed, a pathologist, who is a doctor specialized in analyzing tissues, will examine it. The pathologist will send a report with the results to the consulting doctor. Normal results from a laparoscopy indicate that there is no abdominal bleeding, hernias, or intestinal blockages. It also means that all your organs are in good health.
An appointment will be scheduled with you to go over the results. If a serious medical condition will be found, then he will discuss appropriate treatment options with you. He will work with you to come up with a plan for addressing that condition.